Describe the Structure of the Nuclear Atom
What is the atomic number of an element. A cath- ode ray is also deflected by electrically charged metal plates as shown in Figure 45b.
The Structure Of The Atom Boundless Chemistry
Carbon is described as The chemical element of atomic number 6 a nonmetal that has two main forms diamond and graphite occurs in impure form in charcoal soot and coal and is present in all organic compounds What system is.

. The electrons are distributed around the nucleus and occupy almost all the volume of the atom. Elements such as helium depicted here are made up of atoms. Rutherfords atomic model became known as the nuclear model.
Carbon Atom What is it. In simple terms an atom is a cloud of tiny electrons buzzing round a central much larger nucleus in a series of orbits called shells. Atomic hydrogen The basic unit of a chemical element Such particles as a source of nuclear energy.
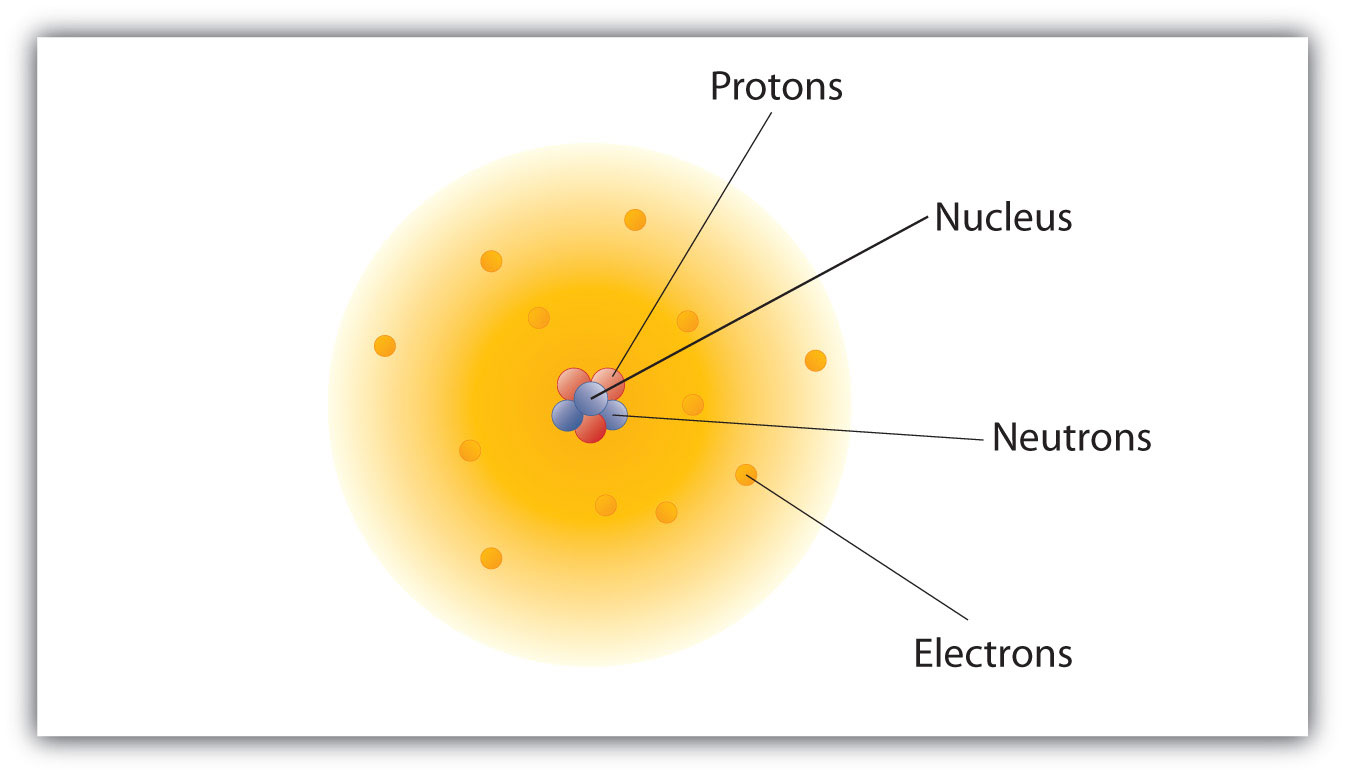
The nucleus is made of one or more protons and a number of neutrons. Structure of an Atom The model of an electric carbon which consists of 6 protons 6 electrons and in most cases 6 neutrons has electrons in simple rings or shells surrounding the nucleus. The rows are called periods and they are numbered from 1 to 7.
114 know what is meant by the terms atom and molecule. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Atoms have a solid core called the nucleus.
It is given the symbol Z. A positively charged plate attracts the cathode ray while a neg-. The shells of an atom are numbered 12 3 and so on starting from the one closest to the nucleus.
Rutherfords Structure of Atom The nucleus is at the center of an atom where most of the charge and mass are concentrated. There are 11 protons and 11 electrons. Describe the Structure of the Atom An atom is the smallest particle of an element which still retains the properties of that element.
In the nuclear atom the protons and neutrons which comprise nearly all of the mass of the atom are located in the nucleus at the center of the atom. According to Daltons atomic theory atoms are composed of protons electrons and neutrons Never True Atoms of elements are electrically neutral Always True The mass of an electron is equal to the mass of a neutron Never True The charge on all protons is the same Always True Negatively charged subatomic particles Electrons. The elements are arranged in seven horizontal rows in order of increasing atomic number from left to right and top to bottom.
The hydrogen atom H contains only one proton one electron and no neutrons. Atomic and Nuclear Structure The atom consists of a small but massive nucleus surrounded by a cloud of rapidly moving electrons. Each shell can occupy a certain number of.
Describe the nuclear model of the atom including the general location of the protons neutrons and electrons the relative size of the nucleus compared to the size of the atom and the modern description of the electron. Each cell represents a different energy level and it can. The nucleus is surrounded by mostly empty space.
115 know the structure of an atom in terms of the positions relative masses and relative charges of sub-atomic particles. The total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atoms atomic number. Structure of an atom.
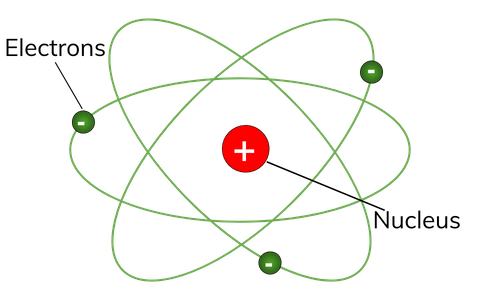
42 Structure of the Nuclear Atom. 116 know what is meant by the terms atomic number mass number isotopes and relative atomic mass Aᵣ. The Rutherford atomic model is known as the nuclear atom.
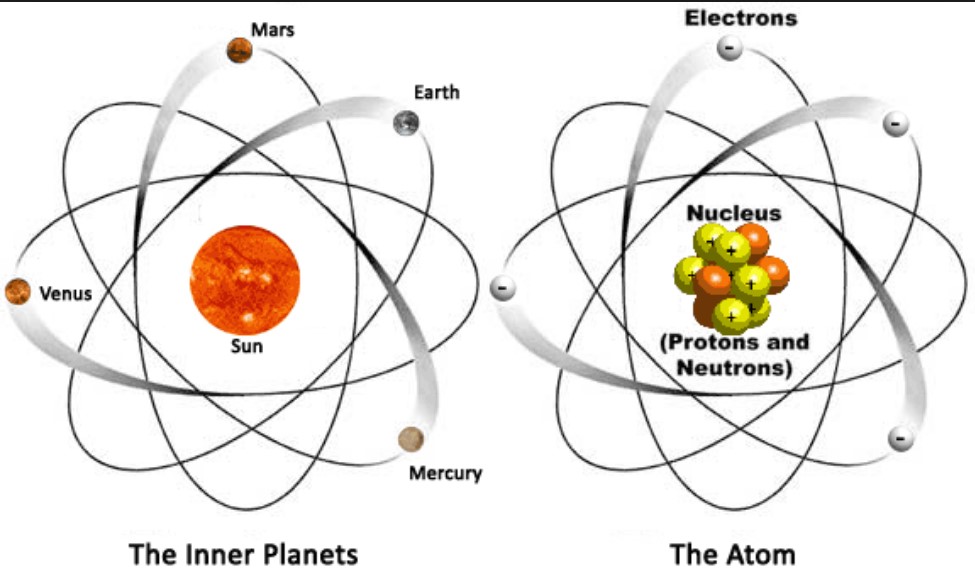
Electrons revolve around the nucleus in a circular orbit similar to the way planets orbit the sun. It is the total number of protons in the nucleus of an element. Structure of the atom Protons neutrons and electrons Atoms are very small.
In the nuclear atom the protons and neutrons are located in the positively charged nucleus. The nucleus is tiny compared to the atom as a. They have a diameter of around 1 10-10 metres m The modern view of.
Structure of the atom Nucleus and shells An atom has a central nucleus. Describe the atomic structure of a neutral sodium atom. The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons.
This is surrounded by electrons arranged in shells. Only the most common variety of hydrogen has no neutrons. The nucleus is the tiny dense central core of the atom and is composed of protons and neutrons.
The Electronic Structure of an Atom Electrons are arranged around the nucleus in the shells of an atom. The nucleus contains two types of sub-atomic particles protons and neutrons. This can be determined using the atomic number and the mass number of the element see the concept on atomic numbers and mass numbers.
Up to 24 cash back STRUCTURE OF THE NUCLEAR ATOM Section Review Objectives Identify three types of subatomic particles Describe the structure of atoms according to the Rutherford model Vocabulary electrons neutrons cathode ray nucleus protons Part A Completion Use this completion exercise to check your understanding of the concepts and terms that are. Every atom is composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus. Atomic of or relating to or comprising atoms.
Section 42 Structure of the Nuclear Atom105 Figure 45a shows how a cathode ray is deflected by a magnet. Start studying Structure of the Nuclear Atom. It is the total number of protons in the nucleus of an element.
Atomic structure is spherical. There are 11 protons and 11 electrons. More than 9994 of an atoms mass is in the nucleus.

Atom Rutherford S Nuclear Model Britannica

Structure Of An Atom Class 9 Science Notes Leverage Edu

Chemical Bonding Atomic Structure And Bonding Britannica

Introduction To Structure Of Atom Proton Neutron Electron With Examples

Atomic Structure Electrons Protons Neutrons And Atomic Models

Nuclear Shell Model Of An Atom Theory Explanation Difference Between Shell Structure Of Nuclei And Shell Structure Of Atom
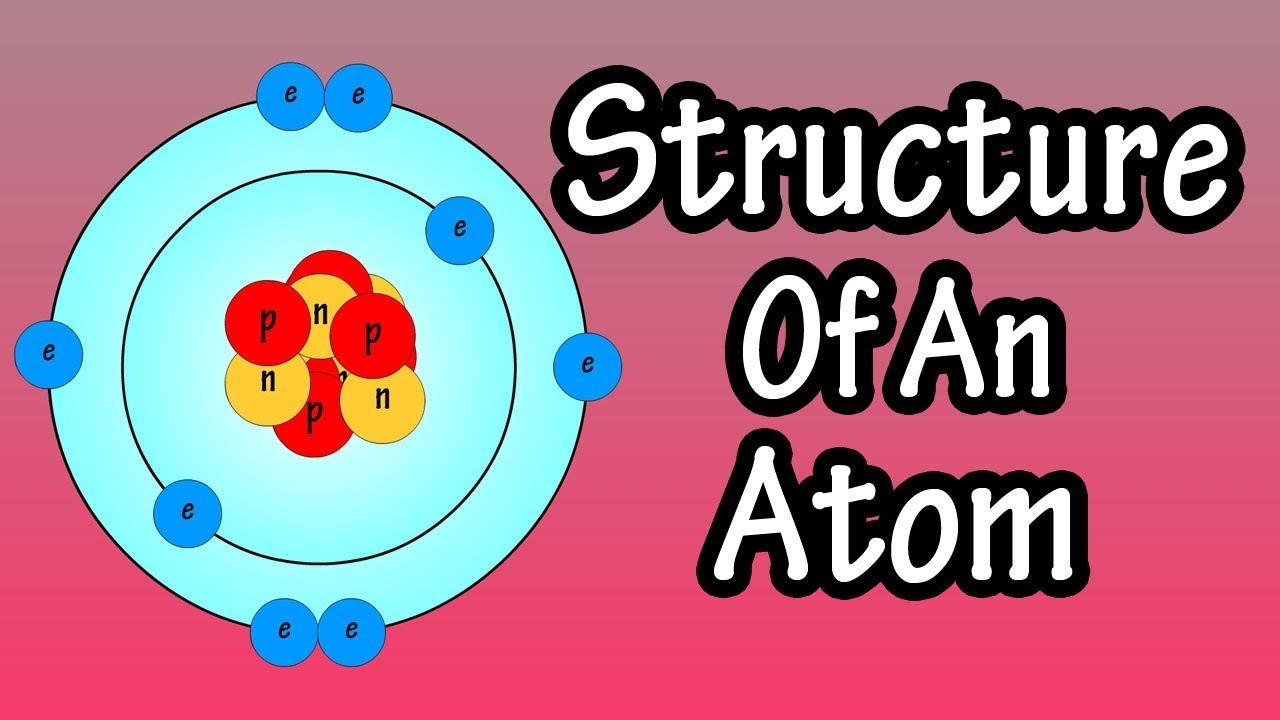
Atomic Structure And Electrons Structure Of An Atom What Are Atoms Neutrons Protons Electrons Youtube

Atomic Models Thomson S Atomic Model And Rutherford S Atomic Model
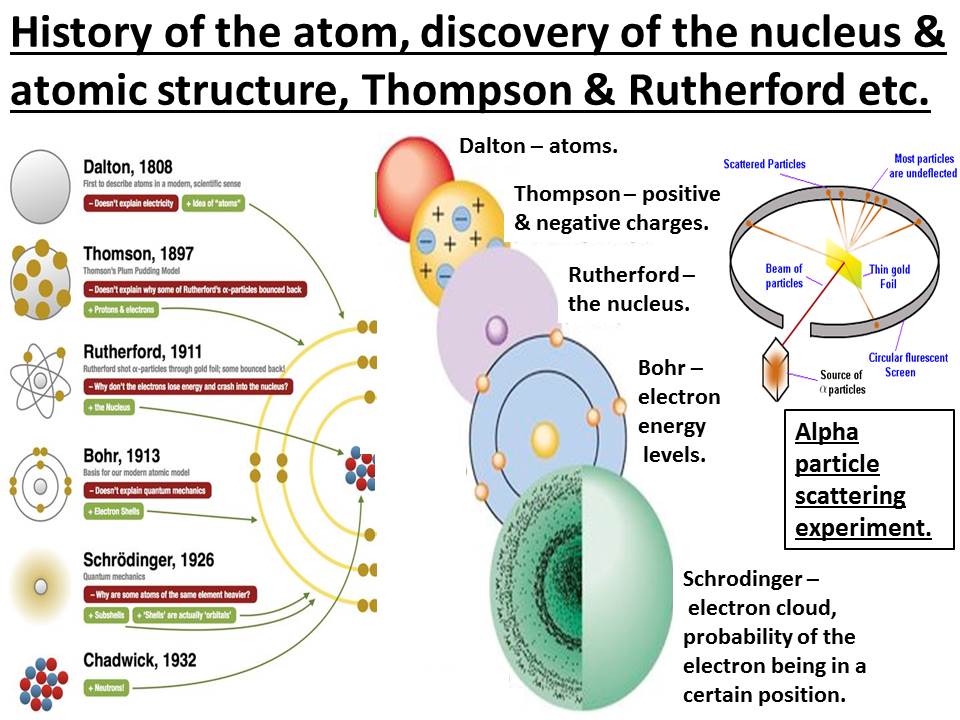
History Of The Atom Discovery Of The Nucleus Thompson Rutherford Alpha Particle Scattering Bohr Teaching Resources

Draw The Structure Of Atom And Explain About It Study Com

Atomic Structure Electrons Protons Neutrons And Atomic Models

Rutherford S Atomic Model Chemistry For Non Majors
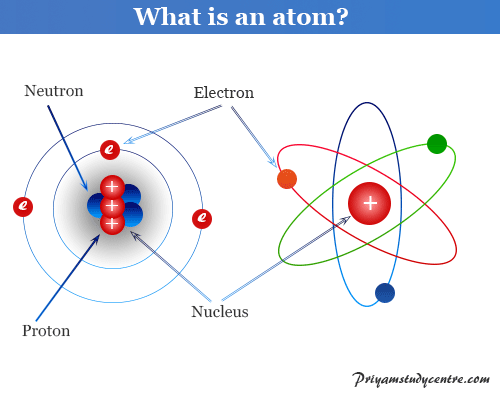
Atom Structure Definition Theory Examples Diagram
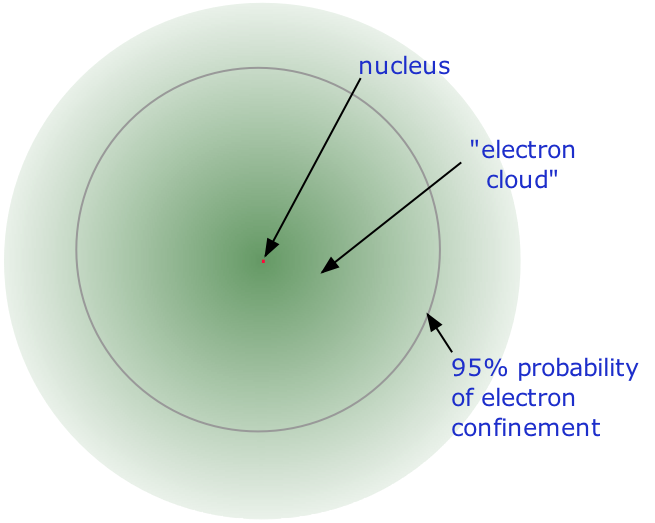
1 2 Principles Of Atomic Structure Review Chemistry Libretexts
What Is Atomic Structure Definition From Seneca Learning

Comments
Post a Comment